|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Path effect |
  
|
|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Path effect |
  
|
 Path effect You can find the path effect in the Toolbox below the tab objects, in the object effects section. The inserted images are arranged in order along a path you have prescribed. |
1. Effect of the path effect 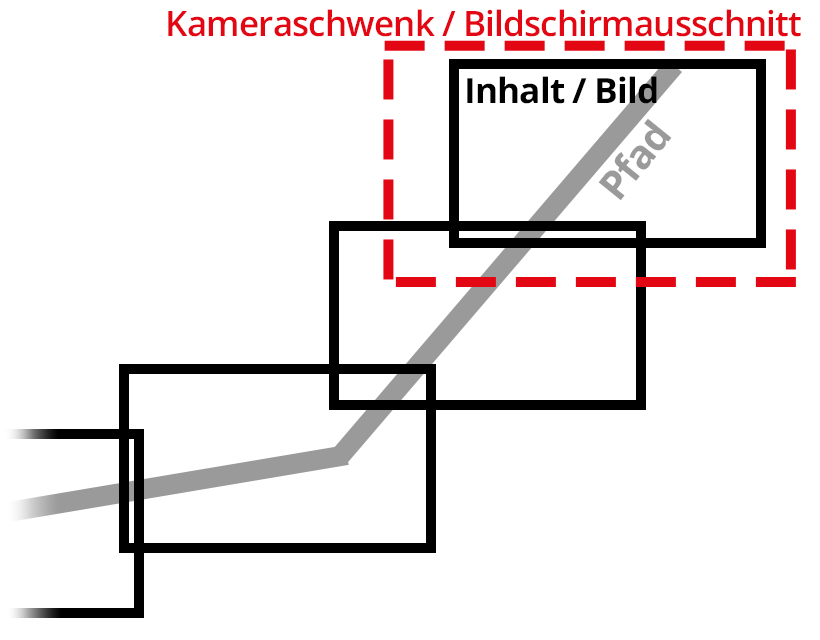 Camera pan across images on a path Inserted images are automatically arranged along a path which you have created. When you play the effect, there will be a camera pan over the inserted images. In the above example, you can see a motion path, which starts at the top right, runs down and then bends to the left. |
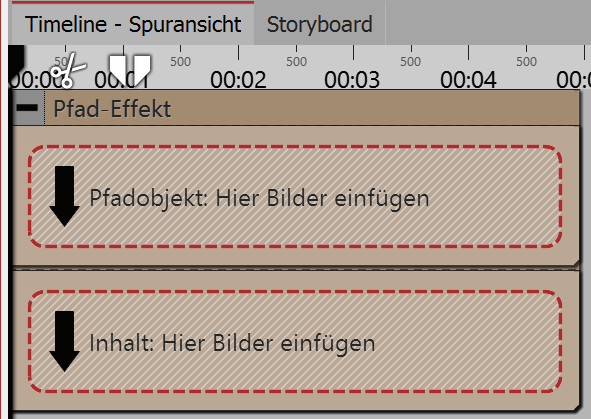 Here the effect has two areas: path object and content. 2.1. Creating a pathDrag any image you want to use to create the path into the path object. The image is not displayed, and only serves to create a motion path. Creating the path with the help of the image. The individual motion markers can also be found in the non-visible portion of the Layout designer. So that you can better use this area, shrink the view in the Layout designer with the minus magnifying glass icon. |
Drag the images or videos that should be on the path into the content area. You can arrange the images here underneath one another to ensure that they are shown at the same time. If the images are arranged one after another, the previous images will fade out after the display time.
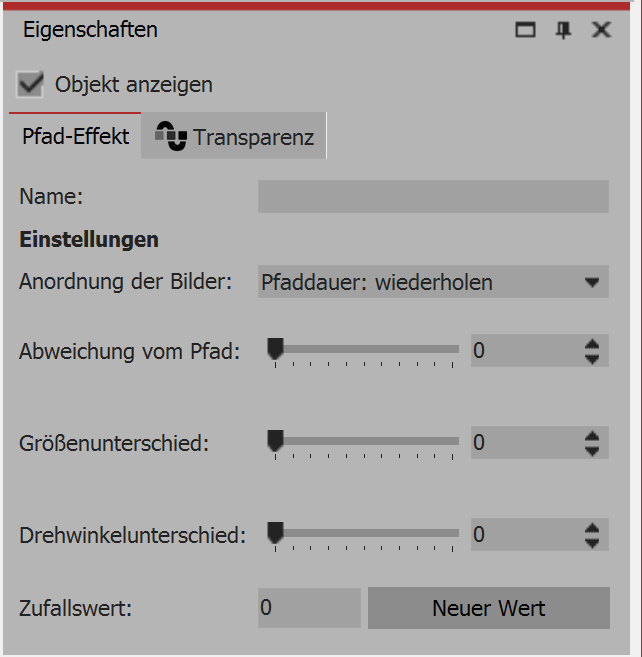
Properties of the path effect
Image order
The images are arranged around the path. The duration of the path is determined by its motion markers. This duration need not correspond to the duration of the path effect. In the case that there is a lack of correspondence, it can be controlled with this option.
Duration of path: repeating - the path is repeated. If the paths is, for example, a circle, the path effect will make more revolutions.
Duration of path: scaling - the path will aligned precisely with the duration of the path effect.
Length of path - the path effect will run for only as long as the length of the path.
Deviation from the path
Specifies how far the objects may be placed on the display away from the predetermined path.
Difference in size
Specifies the allowed difference in size between the objects.
Difference in the angle of rotation
Specifies how far the objects may be rotated.